With increasingly extreme weather patterns, local governments face damage to buildings, housing, bridges, and more, signaling a need to prepare for these costs and protect local budgets. Grant funding can be essential for mitigating the financial strain on local governments, making effective grants research, management, and tooling a worthwhile investment.
What are the Costs of Climate Change?
Given this issue’s vast and complex nature, the specific concerns to infrastructure that local governments face regarding climate change can often be overlooked.

As climate conditions change, natural weather patterns are disrupted and can contribute to devastating weather-related issues like wildfires, which have become more common in recent years.
Adverse weather conditions, such as rising temperatures, drier climates, and heavy rainfall, can contribute to the frequency and severity of natural events including flooding, wildfires, and earthquakes, straining local economies due to rebuilding and restoration efforts.
The damage to infrastructure is a significant monetary burden, costing the U.S. over $150 billion each year. With buildings, homes, and even bridges destroyed, local leaders are required to mobilize quickly and rebuild using funds they may not even have. Given the unpredictability of these disruptions, it can be difficult for agencies to have readily available resources specifically allocated for these circumstances— especially while juggling all the other demands of managing a community.
As financial burdens due to climate change continue to mount, local governments that proactively secure funding will be better prepared to face these inevitabilities. The first step in this process is facilitating improved strategy, as outlined in Strategic Planning in a Time of Change: The Plays, a playbook created in collaboration with Funkhouser & Associates. With strategic leaders and detailed plans for the future, local organizations are then prepared to use a more targeted approach to both budgeting and securing grant funding
Grant funding has proved a key tool in an agency’s arsenal for fighting climate change. Having been identified an essential area of focus, there are billions of dollars worth of funding available specifically for handling climate change. For example, there is $575 million in funding available for building coastal climate resilience. By aligning budgeting strategies with these grants, communities can implement protection plans that not only address immediate needs but also future proof their infrastructure and resources.
What Grant Strategies have Local Communities Implemented?
1. Community Protection Plans
Community Protection Plans involve ideating, creating, and implementing key strategies and processes to ensure that communities are prepared for adverse weather events such as wildfires. With these plans in place, communities have a precedent to follow and can minimize panic, allowing for a solution-focused approach. The State of New Jersey was able to secure $300,000 to support community wildfire adaption through the creation of new and modified wildfire protection plans such as purchasing and outfitting trailers for prescribed burns and awarding subgrants for related projects. The Superior Watershed Partnership was awarded $288,658 to collaborate with private landowners, local governments, state and tribal partners on fire mitigation projects such as hazardous fuel reduction and fire risk assessment for high-priority areas. These previously funded projects are impactful and necessary in preparing communities for climate-related scenarios and even in predicting them.
2. Hazard Mitigation in High-Risk Regions
Higher risk regions, such as Sonoma County, California, have received funding through grants like the Hazard Mitigation Grant Program. The Sonoma County Fire Protection District received $6,716,520 in funding to implement strategies for reducing risk to property and infrastructure from natural hazards such as wildfire and extreme heat. They facilitated a phased vegetation management project to ensure defensible space measures around both residential and non-residential buildings and structure through the removal and reduction of flammable vegetation and hazardous fuel and flammable material reduction. Prevention techniques to reduce the impacts of natural hazards protect local governments from having to scramble for funding and pay for costly repairs after the fact.
3. Improved Community Structure Resilience
The Resilient Communities Program enabled the City of Wimberley to secure $300,000 for a digital living comprehensive plan designed to ensure the development of resilient and flood damage proof building codes. Using digital engagement software in community forums to educate and gather data, conducting housing and land use studies, reviewing zoning ordinances and recommending key revisions, and developing a capital improvement plan facilitated the city’s long-term resilience and prevented inefficient spending in the long run.
These funding examples demonstrate the importance of grants in building resilience for local communities. Facilitating resilience is dependent on ensuring that agencies have the capacity, through both tooling and leadership, to best access funding. A powerful tool for finding and securing funding is Euna’s Grants Network, a professionally curated database of grants.
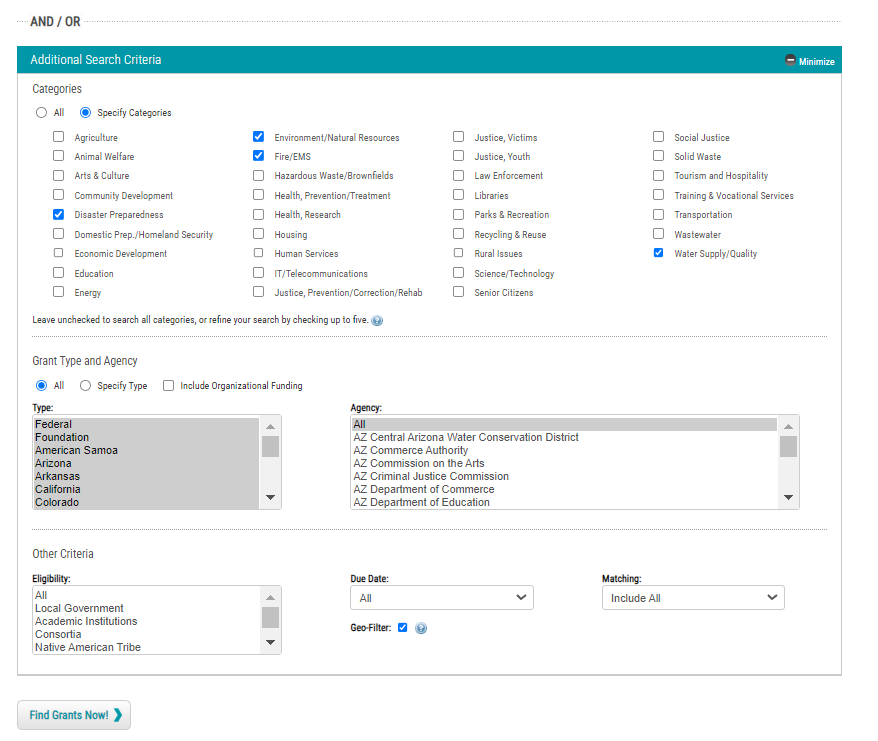
With advanced search and filtering to customize by category, agency, and eligibility, easily find funding that aligns with your community’s goals.
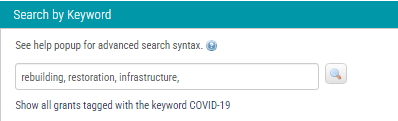
Save time and boost efficiency by using keywords to refine search options to discover the most relevant grant opportunities available.
By implementing key strategies and tools like Euna Grants now, communities will be better protected against whatever the future holds.
Preparing for Adverse Weather Events: The Role of Public Sector Budgeting
As climate change continues to escalate, local governments face the increasing challenge of preparing for and responding to weather events that are more frequent and more destructive than ever before. Effective budgeting plays a crucial role in ensuring cities and counties are ready to handle the financial impacts of these events. One powerful feature that can aid in this preparation is Scenario Planning, available in Euna Budget Professional.
Scenario Planning: Navigating Uncertainties
Scenario Planning allows public sector agencies to explore “What-If” scenarios by creating hypothetical budgets that anticipate various outcomes. This tool is invaluable for preparing for extreme weather events, as it enables agencies to:
- Compare Different Budget Scenarios: Agencies can model potential financial outcomes based on different extreme weather scenarios. This comparison helps them understand the financial impact of events like hurricanes, wildfires, or flooding, and plan accordingly.
- Improve Decision-Making: By analyzing the impact of various scenarios, agencies can make informed decisions about resource allocation, emergency preparedness, and infrastructure investments. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks and reduces the long-term costs of disaster response and recovery.
- Model Compensation Scenarios: Using the duplicate organization feature, agencies can model different compensation scenarios, such as the costs associated with emergency services, public safety personnel, and recovery operations. This detailed planning ensures that funds are appropriately allocated and ready for deployment when needed.
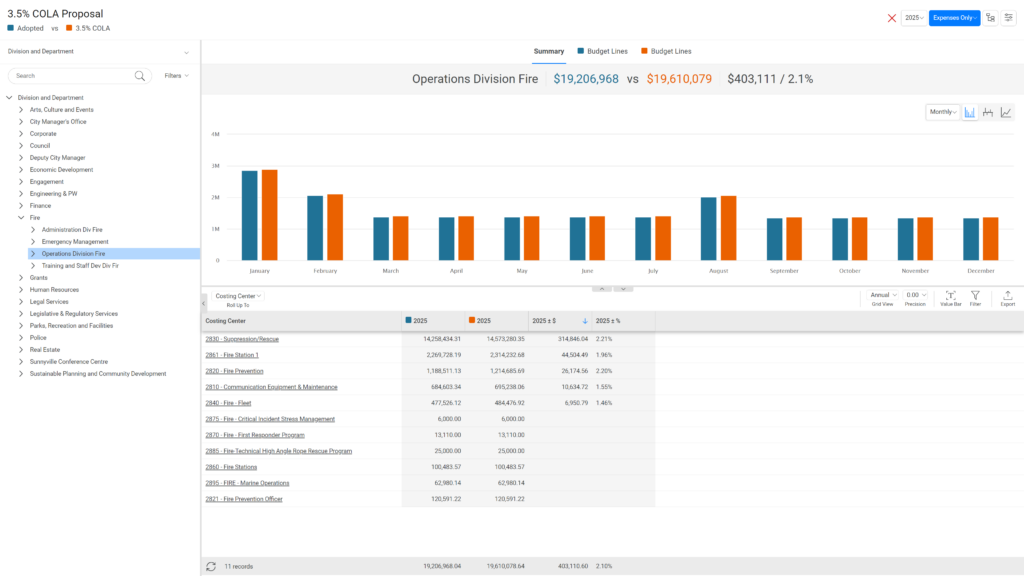
Plan for any scenario, from cost-of-living adjustments (COLA) to unexpected weather or natural disaster events. With the Scenario Planning tool, you can model ‘What-If’ budgets to navigate uncertainties and make informed decisions with confidence.
Insightful Comparisons with the Comparison Tool
Following the development of various “What-If” scenarios, the next crucial step is using the Comparison Tool. This feature allows agencies to:
- Compare Budget Scenarios: Analyze differences between the adopted budget and hypothetical budgets for various extreme weather scenarios. This tool enables a direct comparison of potential financial impacts, helping identify potential funding gaps and the need for additional resources.
- Assess Preparedness: By contrasting different “What-If” budgets, agencies can gauge their preparedness for extreme weather events. This comparison ensures that sufficient funds are allocated to emergency response and recovery efforts, minimizing financial shortfalls during crises.
Reserve Planning: A Critical Component of Scenario Planning
By analyzing these scenarios, agencies gain valuable insights into the financial resources required to manage potential events, enabling them to make informed decisions about the amount of reserves they need to set aside. Scenario Planning also plays a crucial role in reserve planning, which is essential for maintaining financial stability during crises. This process allows agencies to:
- Estimate Emergency Response Costs: Determine the amount needed in a disaster reserve fund based on potential costs of emergency services and recovery efforts.
- Set Reserve Targets: Establish specific targets for reserve funds to ensure financial readiness for various disaster scenarios.
- Adjust for Future Trends: Consider inflation and other cost increases, adjusting reserve targets to maintain adequate funding over time.
Scenario Planning and reserve planning are vital tools for public sector agencies facing the escalating challenges of climate change. By modeling various “What-If” scenarios, agencies can anticipate the financial impacts of extreme weather events and other climate-related disruptions. This approach enables them to prioritize risks, allocate resources effectively, and set aside appropriate reserves to address emergencies. As climate change intensifies, causing more frequent and severe weather events, these strategies ensure that agencies are not only prepared for immediate crises but also support long-term community resilience and financial stability. Through proactive planning, agencies can better protect critical infrastructure and maintain essential services, safeguarding their communities against the uncertainties of a changing climate.
How can my Community Cut Future Costs and be Prepared?
All the grants mentioned above, as well as the details of previously funded projects, are available within the Euna Grants Network. Euna Grants is a full lifecycle grants management tool purpose-built for the public sector. With increasing volumes of climate change-related grants, the Grants Network search and filtering software, along with examples of previously funded applications ensure finding and securing funding that support your community’s specific challenges, be it risk mitigation, infrastructure development and more to prepare for extreme weather events. Once these grants are awarded, easily manage and give funding to maximize community impact through Euna Grants’ Post-Award Management and Subrecipient Management tools.
However, securing grants is only part of the solution. Integrating these funds into a comprehensive budget plan ensures that communities are not only prepared for adverse weather events but are also financially resilient in the face of unpredictable challenges.
By prioritizing future-focused budgeting and proactive approaches to receiving climate change funding, local governments can ensure that their communities remain prepared for whatever the future holds.
Learn more about Euna’s Grants and Budgeting Solutions to support your community’s plans for resilience to extreme weather patterns.